In my reading experience, the definitive account of the outbreak of The Great War remains Barbara Tuchman’s The Guns of August (1962). The author made us flies on the wall in cabinet meeting rooms across Europe, and hidden observers within General Staff offices of the armies of Germany, Britain, France and Russia. This book is very different. Its premise is that this was a truly global conflict, principally due to the vast colonial outreach of the major powers. Men and women, ordinary citizens of places in Africa that were ruled from London, Berlin, Paris and Brussels, remote settlements in the Caucuses who were subject to the rule of the Tsar, shoeless peasants in the outer reaches of the ailing Ottoman empire, and those living in the United States and South America who were part of the colossal diaspora from Europe – all felt the rough hand of destiny on their shoulder.
The celebrated (but not always admired) historian AJP Taylor famously argued that the outbreak of the war was inevitable, due to military planning relying on inflexible railway timetables. Once the trains, packed with tens of thousands of men, headed off to their destination, then conflict was inevitable. This theory is easily challenged but Churchill and Eberholst give this example:
Britain’s rail network comprised some 23,000 miles of track. On 4th August 1914, 130 companies were effectively taken over by the government. At Aldershot, from 5th August officers were being handed dossiers that revealed the plan for their departure. For instance: ‘Train No 463Y will arrive at siding B at 12.35 a.m., 10th August. You will complete loading by 3.40 a.m.’
Britain’s army in 1914 was tiny compared to those of France, Germany and Russia. It was even outnumbered by the army of Belgium, but it was superbly trained and had relatively recent battlefield experience in the Boer Wars. The key difference between Britain and the empires of France and Germany was in the existence of Britain’s white dominions. Australia, Canada, New Zealand and South Africa were, in theory at least, at one with the mother country’s foreign policy.
One of the many valid points made by the authors is the vexatious question of perceived neutrality. Long before the first shots were fired in the war, developed nations needed vast quantities of imports and, were they fortunate enough to possess natural resources, ships to export material and goods elsewhere. The ownership of cargo vessels was perhaps not as opaque then as it is now but, for example, if a Swedish ship sailed into Hamburg loaded with iron ore, did that compromise Sweden’s notional neutrality? What if an American ship loaded with wheat were headed for the Port of London? Did that make the vessel fair game for German submarines?
The authors remind us that by the time the trenches ran from Switzerland to the Belgian coast, maps were able to be made showing every dip or fold in the land and – literally – every large shell crater. In the dying days of August 1914, particularly in the rural areas of Galicia, East Prussia and Serbia, the landscape was a complete mystery to field commanders. Knowledge of the terrain was almost completely absent, resulting in disastrous tactical blunders by all sides.
Comparing different kinds of horror brought about by war is, perhaps, futile, but as an amateur historian brought up on grim tales of life in the Western Front trenches, I was struck by the descriptions of the relentless carnage of these early weeks of the war. Yes, it was a war of movement but, in particular, it was fought in intense August heat. Men on the march were driven mad by thirst; tinder-dry fields and woods caught fire quickly, cremating the dead and wounded alike. This was a new kind of war; medical services were woefully inadequate to meet carnage on this scale. I was quickly disabused of any notions I had that these early battles between the huge armies were somehow cleaner and less grisly than the trench warfare which followed them.
Another surprise (at least to this woefully ignorant reader) was to learn that Japan and Britain fought together to drive Germany out of Chinese city of Tsingtao (below) between August and November 1914. It is a sobering reflection on the fragile nature of national alliances to think that less than a decade earlier, Japan and Russia locked horns in a savage war. Now, they were, notionally, allies in a war against Germany.
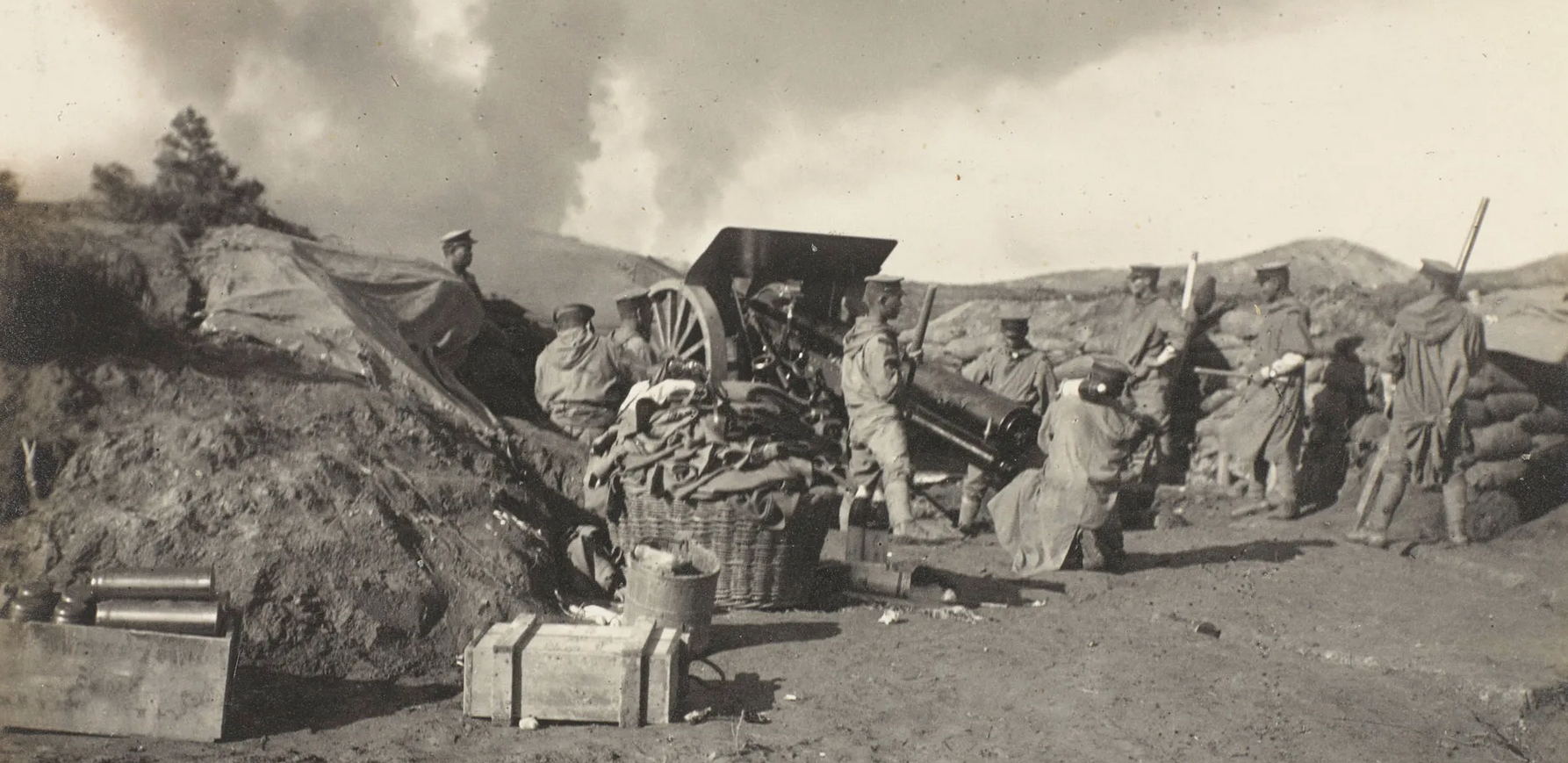

As autumn turned into winter, the major powers were all unsteady on their feet. The French had suffered astonishing losses in the east, but had engineered a miracle on The Marne. Germany’s relentless advance through Belgium had been thwarted, and they had back-pedalled in disarray to dig in north of The Aisne. Despite the debacle at Tannenberg, Russia had inflicted a monstrous defeat on Austria Hungary in Galicia. This account, from a Hapsburg officer, is horrific :
‘Scenes from Dante’s Inferno were happening on the road. Driven by instinct, both men and horses pressed forward, regardless of the corpses and wounded lying on the ground. Horses hooves were treading over bellies and heads. Intestines, guts, brains mixed with mud covered the road with a bloody mess. The screams of the wounded, men and horses, together with the cracking rifles, grenade and shell explosions drove one to near insanity.’
I am always intrigued by writing partnerships, and ponder the (largely irrelevant) question, “Who did what?” Whatever the respective inputs were here, Churchill and Eberholst have written a book that is historically authoritative but always accessible. UK Great War literature tends, for quite laudable reasons, centred on the Western Front and the great calamities that took place there, but here we have a timely reminder of the days before the trenches were dug “from Switzerland to the sea” and the horrific slaughter that took place in places with names that have long since vanished from the map. Ring of Fire will be published by Apollo on 8th May.














 Investigator and journalist Harry Lark fought for King and Country and emerged relatively unscathed although, like so many other men, the sounds, smells and images of the trenches are ever present at the back of his mind and he has also become addicted to laudanum – a tincture of opium and alcohol. When he is contacted by a friend and benefactor, Lady Charlotte Carlisle, she tells him that she thinks she has seen a ghost. Sitting in Mayfair’s Café Boheme, she has seen a man who is the image of Captain Adrian Harcourt, a pre-war politician who was killed on the Western Front in 1918, and was engaged to be married to her daughter Ferderica. But this man is no phantom who can fade into the wallpaper. Other customers notice him. He is flesh and blood, and approaches Lady Charlotte’s table, stares into her eyes, but then leaves without saying a word. She asks Lark to investigate.
Investigator and journalist Harry Lark fought for King and Country and emerged relatively unscathed although, like so many other men, the sounds, smells and images of the trenches are ever present at the back of his mind and he has also become addicted to laudanum – a tincture of opium and alcohol. When he is contacted by a friend and benefactor, Lady Charlotte Carlisle, she tells him that she thinks she has seen a ghost. Sitting in Mayfair’s Café Boheme, she has seen a man who is the image of Captain Adrian Harcourt, a pre-war politician who was killed on the Western Front in 1918, and was engaged to be married to her daughter Ferderica. But this man is no phantom who can fade into the wallpaper. Other customers notice him. He is flesh and blood, and approaches Lady Charlotte’s table, stares into her eyes, but then leaves without saying a word. She asks Lark to investigate. company, and that some seriously well-connected people have ensured that the truth about their demise has been successfully covered up. Iver’s son has been committed to an institution for mentally and physically damaged WW1 soldiers, and Filton Hall is Harry’s next port of call.
company, and that some seriously well-connected people have ensured that the truth about their demise has been successfully covered up. Iver’s son has been committed to an institution for mentally and physically damaged WW1 soldiers, and Filton Hall is Harry’s next port of call.

 England, 1923. Like thousands upon thousands of other young women, Esme Nicholls is a widow. Husband Alec lies in a functional grave in a military cemetery in Flanders. His face remains in a few photographs, and in her memories. Left penniless, she ekes out a living by writing a nature-notes feature for a northern provincial newspaper, and serving as a personal assistant to an older widow, Mrs Pickering. Mrs P has the advantage of being able to visit her husband’s grave whenever she wants, as he was not a victim of the war.
England, 1923. Like thousands upon thousands of other young women, Esme Nicholls is a widow. Husband Alec lies in a functional grave in a military cemetery in Flanders. His face remains in a few photographs, and in her memories. Left penniless, she ekes out a living by writing a nature-notes feature for a northern provincial newspaper, and serving as a personal assistant to an older widow, Mrs Pickering. Mrs P has the advantage of being able to visit her husband’s grave whenever she wants, as he was not a victim of the war. Caroline Scott (right) treats us to a high summer in Cornwall, where every flower, rustle of leaves in the breeze and flit of insect is described with almost intoxicating detail. Readers who remember her previous novel When I Come Home Again will be unsurprised by this detail. In the novel, she references that greatest of all poet of England’s nature, John Clare, but I also sense something of Matthew Arnold’s poems The Scholar Gypsy and Thyrsis, so memorably set to music by Ralph Vaughan Williams.
Caroline Scott (right) treats us to a high summer in Cornwall, where every flower, rustle of leaves in the breeze and flit of insect is described with almost intoxicating detail. Readers who remember her previous novel When I Come Home Again will be unsurprised by this detail. In the novel, she references that greatest of all poet of England’s nature, John Clare, but I also sense something of Matthew Arnold’s poems The Scholar Gypsy and Thyrsis, so memorably set to music by Ralph Vaughan Williams.



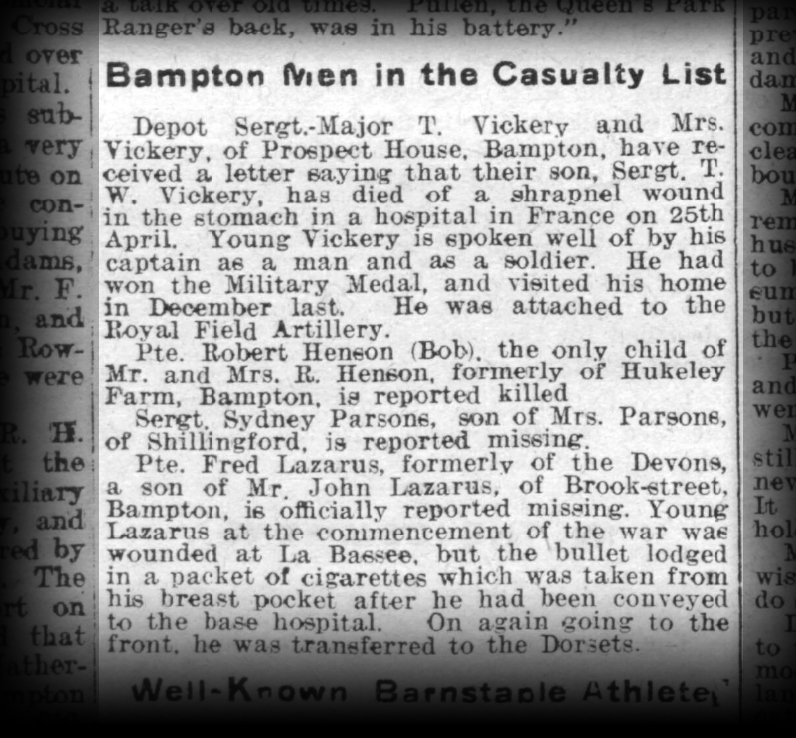

 Robert’s regiment, The Somerset Light Infantry, has a distinguished history. It was founded in 1685 as part of King James II’s response to the Monmouth Rebellion. Under various titles it fought in every major conflict including the Napoleonic Wars, the Crimean War, the Afghan Wars and the Boer War until it was finally merged with other regiments to become The Light Infantry in 1968.
Robert’s regiment, The Somerset Light Infantry, has a distinguished history. It was founded in 1685 as part of King James II’s response to the Monmouth Rebellion. Under various titles it fought in every major conflict including the Napoleonic Wars, the Crimean War, the Afghan Wars and the Boer War until it was finally merged with other regiments to become The Light Infantry in 1968.


















