The year of 1926 was not a particularly momentous one for Wisbech.The canal was officially closed, the first cricket match was played on the Harecroft Road ground, and greyhound racing came to South Brink. For one Wisbech family, the year would bring a trauma that would haunt them for the rest of their lives
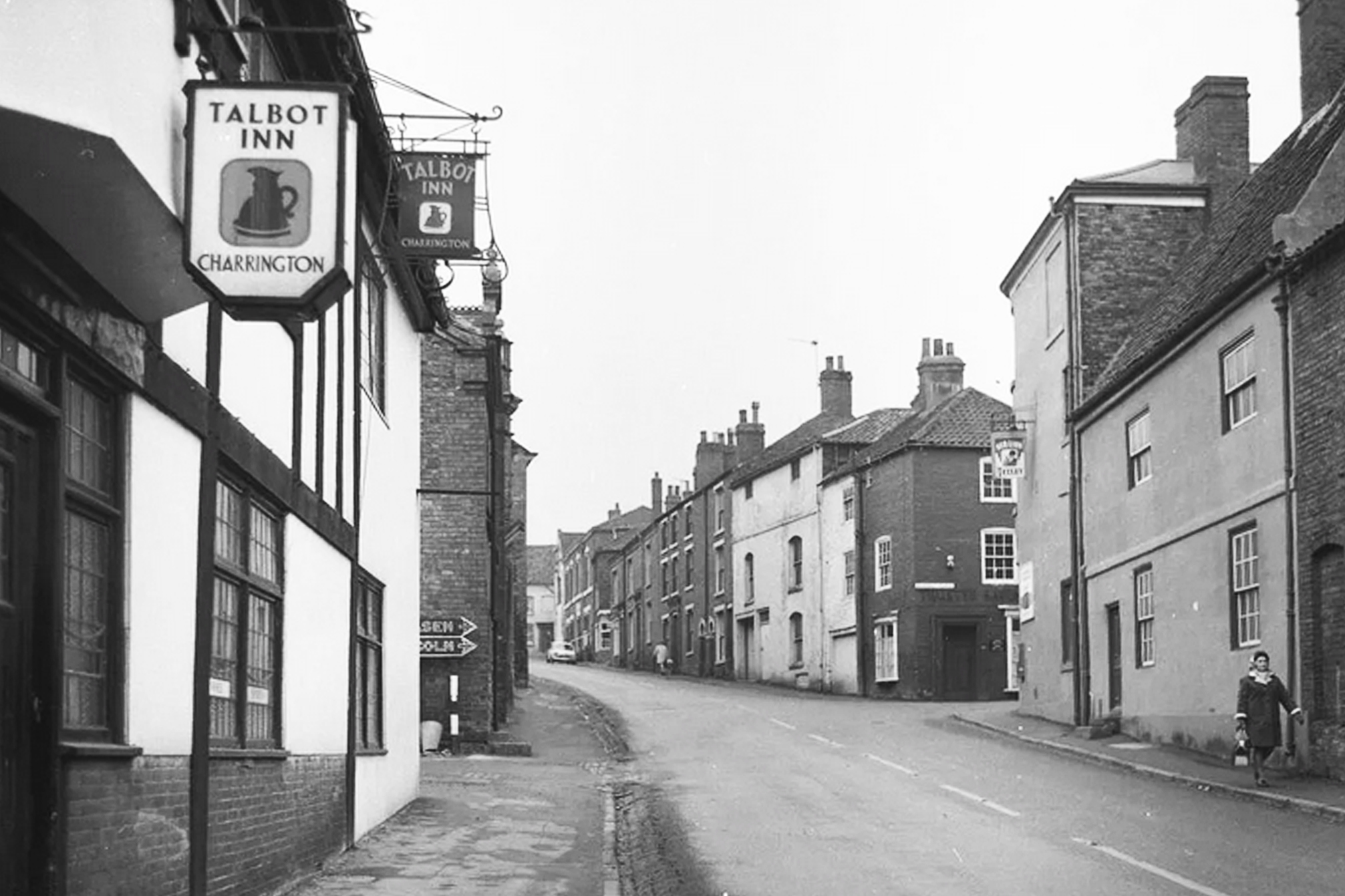
The Corn Metre Inn, like dozens of other pubs from Wisbech’s history, is long gone. It had two entrances, one more or less opposite Nixon’s woodyard on North End, and the other facing the river on West Parade. The name? A Corn Metre was a very important person, back in the day. He was basically a weights and measures inspector employed by markets and auctioneers to ensure that no-one was cheating the customers.
In 1926, the landlord of the Corn Metre was Francis William Noble. He was not a Wisbech man, having been born in Shoreditch, London in 1885. He had met and married his wife Edith Elizabeth (née Bradley) in nearby West Ham in 1907. Noble volunteered for service in The Great War, and survived. By 1910 the couple had moved to Wisbech.

The 1921 census tells us that the family was living at 73 Cannon Street, that Noble was a warehouseman for Balding and Mansell, printers, and that living in the house were Edith Violet Noble (12), Phyllis Eleanor Noble (9) and Francis William Noble (6). Another daughter, Margaret Doris was born in 1923, and by 1926 the family had moved in as tenants of The Corn Metre Inn. A local newspaper reported on the events of Tuesday 15th June:

What they saw was truly horrendous. Propped up on the bed was Mrs Noble, covered in blood with terrible wounds to the throat. But beside the bed was something far worse. In a cot was little Peggy Noble. And her head had been almost severed from her body. She was quite clearly dead. The police were fetched, and then a doctor. Mrs Noble was still alive, and was rushed to the North Cambs Hospital, where she died on the Wednesday Evening.
I suppose that the treatment and awareness of mental health issues has advanced since 1926. It must have, mustn’t it? I am reminded of the tragic murder/suicide In Wimblington in 1896 (details here) when a distraught mother killed herself and her four children. Sadly, there are cases today where mental health treatment is frequently misguided and inadequate. In 2023 Nottingham killer Valdo Calocane was a patient of the local mental health trust. He killed three people in a psychotic attack. There was talk, in 1926, that Edith was ‘unwell’ and that neighbours had been looking in on her. The last note written by Edith is chilling, and is clearly the work of a woman in distress. It was in some ways, however, crystal clear, and written by someone who was aware of the consequences of what she was about to do.

So many unanswered questions. So many things we will never know. Why did she think that Peggy was too young to survive with husband Francis and the other children? It is also revealing that she referred to the 8 year-old boy as ‘Son’, rather than his given name, Francis.
For reasons that can be imagined Francis Noble had had enough of Wisbech, because records show that in February 1928 he remarried, in Rochester His bride was a widow, Beatrice Emily Gadd. In July of that same year, Beatrice gave birth to a son, Peter Eddie. As the Americans say, ‘do the math”.
It is not for me, or any modern commentator to cast blame. Three things stand out, however. Firstly, the three surviving children left Wisbech as soon as they were able, and each appeared to have led perfectly ordinary lives in other parts of the country. Second, Francis Noble, within months of the terrible event at The Corn Metre had left the town, and impregnated another woman who, to be fair, he then married. Thirdly – and this part of the story will haunt me for a long time – poor little Margaret ‘Peggy’ Noble was so savagely cut with the razor that her spinal cord was severed. The coroner, in measured words, recorded that her body bore signs of a violent struggle. What kind of anger, despair and rage fuelled the assault on that little girl? And what was the cause?




 SO FAR: In the early hours of Monday 2nd February 1976, the butchered body of Chinese nurse Tze Yung Tong (left) was found in her room in a nurses’ hostel at 83 Redford Road, Leamington Spa. Other young women had heard noises in the night, but had been too terrified to venture beyond their locked doors. We can talk about ships passing in the night, in the sense of two people meeting once, but never again. Tze Yung Tong was to meet her killer just the one fatal time.
SO FAR: In the early hours of Monday 2nd February 1976, the butchered body of Chinese nurse Tze Yung Tong (left) was found in her room in a nurses’ hostel at 83 Redford Road, Leamington Spa. Other young women had heard noises in the night, but had been too terrified to venture beyond their locked doors. We can talk about ships passing in the night, in the sense of two people meeting once, but never again. Tze Yung Tong was to meet her killer just the one fatal time.
 Despite his palpable guilt, Reilly was endlessly remanded, made numerous appearances before local magistrates, but eventually had brief moment in a higher court. At Birmingham Crown Court in December, Mr Justice Donaldson (right) found him guilty of murder, and sentenced him to life, with a minimum tariff of 20 years.In 1997, a regional newspaper did a retrospective feature on the case. By then, the police admitted that he had already been released. Do the sums. Reilly, the Baby-Faced Butcher may still be out there. He will only be in his late 60s. Ten years younger than me. One of the stranger aspects of this story is that, as far as I can tell, at no time did solicitors and barristers working to defend Reilly ever suggest that his actions were that of someone not in his right mind. By contrast, in an earlier shocking Leamington case in 1949,
Despite his palpable guilt, Reilly was endlessly remanded, made numerous appearances before local magistrates, but eventually had brief moment in a higher court. At Birmingham Crown Court in December, Mr Justice Donaldson (right) found him guilty of murder, and sentenced him to life, with a minimum tariff of 20 years.In 1997, a regional newspaper did a retrospective feature on the case. By then, the police admitted that he had already been released. Do the sums. Reilly, the Baby-Faced Butcher may still be out there. He will only be in his late 60s. Ten years younger than me. One of the stranger aspects of this story is that, as far as I can tell, at no time did solicitors and barristers working to defend Reilly ever suggest that his actions were that of someone not in his right mind. By contrast, in an earlier shocking Leamington case in 1949, 






 Sybil (right) was born in the summer of 1930, and grew up with her family in their house in the relatively comfortable Gateshead suburb of Felling. The few contemporary pictures which were published in newspapers at the time of her death show an attractive and confident young woman. At some point after WW2, she was courted by John Docherty, a few years her senior, who worked as a despatch clerk with a local firm. He was not in the best of health, and had been diagnosed with what Victorians called consumption. We now know it as tuberculosis and, despite reported occurrences of the disease within immigrant communities, it has now been conquered by immunisation. Docherty and Sybil became engaged, but at some point in the spring of 1954, Sybil had second thoughts, broke off the engagement and returned to Docherty the ring, and various other gifts.
Sybil (right) was born in the summer of 1930, and grew up with her family in their house in the relatively comfortable Gateshead suburb of Felling. The few contemporary pictures which were published in newspapers at the time of her death show an attractive and confident young woman. At some point after WW2, she was courted by John Docherty, a few years her senior, who worked as a despatch clerk with a local firm. He was not in the best of health, and had been diagnosed with what Victorians called consumption. We now know it as tuberculosis and, despite reported occurrences of the disease within immigrant communities, it has now been conquered by immunisation. Docherty and Sybil became engaged, but at some point in the spring of 1954, Sybil had second thoughts, broke off the engagement and returned to Docherty the ring, and various other gifts.
 Historian and broadcaster Tony McMahon (left) sets out his stall in this book, and he is selling a provocative premise. It is that a celebrity fraudster, predatory homosexual, quack doctor and narcissist – Francis Tumblety – was instrumental in two of the greatest murder cases of the 19th century.The first was the assassination of Abraham Lincoln in April 1865, and the second was the murder of five women in the East End of London in the autumn of 1888 – the Jack the Ripper killings.
Tumblety was certainly larger than life. Tall and imposingly built, he favoured dressing up as a kind of Ruritanian cavalry officer, with a pickelhaub helmet, and sporting an immense handlebar moustache. He made – and lost – fortunes with amazing regularity, mostly by selling herbal potions to gullible patrons. Despite his outrageous behaviour, he does not seem to have been a violent man. Yes, he could have been accused of manslaughter after people died from ingesting his elixirs, but apart from once literally booting a disgruntled customer out of his suite, there is no record of extreme physical violence.
Historian and broadcaster Tony McMahon (left) sets out his stall in this book, and he is selling a provocative premise. It is that a celebrity fraudster, predatory homosexual, quack doctor and narcissist – Francis Tumblety – was instrumental in two of the greatest murder cases of the 19th century.The first was the assassination of Abraham Lincoln in April 1865, and the second was the murder of five women in the East End of London in the autumn of 1888 – the Jack the Ripper killings.
Tumblety was certainly larger than life. Tall and imposingly built, he favoured dressing up as a kind of Ruritanian cavalry officer, with a pickelhaub helmet, and sporting an immense handlebar moustache. He made – and lost – fortunes with amazing regularity, mostly by selling herbal potions to gullible patrons. Despite his outrageous behaviour, he does not seem to have been a violent man. Yes, he could have been accused of manslaughter after people died from ingesting his elixirs, but apart from once literally booting a disgruntled customer out of his suite, there is no record of extreme physical violence. Tumblety (right( was a braggart, a charlatan, a narcissist and a predatory homosexual abuser of young men. Tony McMahon makes this abundantly clear with his exhaustive historical research. What the book doesn’t do, despite it being a thrilling read, is explain why the obnoxious Tumblety made the leap from being what we would call a bull***t artist to the person who killed five women in the autumn of 1888, culminating in the butchery that ended of the life Mary Jeanette Kelly in her Miller’s Court room on the 9th November. Her injuries were horrific, and the details are out there should you wish to look for them. As for Lincoln’s homosexuality – and his syphilis – the jury has been out for some time, with little sign that they will be returning any time soon. McMahon is absolutely correct to say that syphilis was a mass killer. My great grandfather’s death certificate states that he died, aged 48, of General Paralysis of the Insane. Also known as Paresis, this was a euphemistic term for tertiary syphilis. The disease would be contracted in relative youth, produce obvious physical symptoms, and then seem to disappear. Later in life, it would manifest itself in mental incapacity, delusions of grandeur, and physical disability. Lincoln was 56 when he was murdered and, as far as we know, in full command of his senses. I suggest that were Lincoln syphilitic, he would have been unable to maintain his public persona as it appears that he did.
Tumblety (right( was a braggart, a charlatan, a narcissist and a predatory homosexual abuser of young men. Tony McMahon makes this abundantly clear with his exhaustive historical research. What the book doesn’t do, despite it being a thrilling read, is explain why the obnoxious Tumblety made the leap from being what we would call a bull***t artist to the person who killed five women in the autumn of 1888, culminating in the butchery that ended of the life Mary Jeanette Kelly in her Miller’s Court room on the 9th November. Her injuries were horrific, and the details are out there should you wish to look for them. As for Lincoln’s homosexuality – and his syphilis – the jury has been out for some time, with little sign that they will be returning any time soon. McMahon is absolutely correct to say that syphilis was a mass killer. My great grandfather’s death certificate states that he died, aged 48, of General Paralysis of the Insane. Also known as Paresis, this was a euphemistic term for tertiary syphilis. The disease would be contracted in relative youth, produce obvious physical symptoms, and then seem to disappear. Later in life, it would manifest itself in mental incapacity, delusions of grandeur, and physical disability. Lincoln was 56 when he was murdered and, as far as we know, in full command of his senses. I suggest that were Lincoln syphilitic, he would have been unable to maintain his public persona as it appears that he did.